Electrostatically promoted dynamic hybridization of glucans with cationic polythiophene†
Abstract
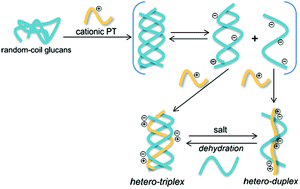
Hybridizing natural macromolecules with synthetic polymers is an efficient general method for constructing sophisticated supramolecular architectures. To comprehensively elucidate the controversial hybridization mechanism of glucans with synthetic polymers, the hybridization behaviors of triple-stranded curdlan (Cur) and schizophyllan (SPG) with cationic polythiophene (PyPT) were investigated in aqueous DMSO solutions by using UV-vis, circular dichroism (CD), fluorescence, fluorescence excitation, and NMR spectroscopy methods, as well as theoretical calculations, dynamic light scattering, and zeta potential measurements. Upon mixing with glucan, a hetero-triplex formed, which was dynamic and greatly accelerated by heating and by adding a base or a salt. The hetero-triplex disassembled into a hetero-duplex in highly basic solutions. Thus, polycationic polymers, such as PyPT, are expected to serve as a versatile tool for unzipping glucan homo-triplexes and promoting subsequent hybridization in aqueous solution, while the detailed mechanism elucidated in the present study contributes to the rational design of hybridization partners.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...